Cytoskeleton comprises of different interconnected protein fibers, shaping a complicated organization spreading all through the cytosol, from the core to the inward flyer of plasma film. Presence of these components inside the cell was shown by electron microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. Cytoskeletal fibers can be seen in live cells with the assistance of refined methods like live cell fluorescence imaging utilizing fluorescent proteins, for example, GFP. The GFP protein is gotten from jellyfish
Aquaria Victoria and is a truly steady protein, along these lines it is utilized as a cell or tissue explicit marker. It was known before that 20-30% of cytoplasm involves proteins, but next to no was perceived about their enzymatic action and underlying or utilitarian jobs. The presence of cytoskeleton was uncovered by complex analytical methods like fluorescent microscopy, electron microscope imaging and advanced video microscopy in the eukaryotic cell.
The fibers are liable for the arrangement of cleavage wrinkle that prompts the division of cytoplasm during cytokinesis in creature cells. They are the key components comprising the contractile fibers of muscle cells, where they participate in trademark muscle constrictions in relationship with myosin fibers.
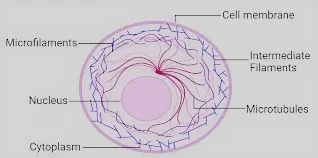
Microfilaments
Are comprised of a protein, known as actin, which establishes the significant protein bit of cytoskeleton. Actin fibers are found in extraordinary numbers just beneath the plasma film where they are coordinated into an organization to confer mechanical strength and backing to the cell. Individual actin monomers are named as G-actin (globular actin) Under ideal physiological conditions, singular actin.
Monomers polymerize into fibers (or microfilaments) Actin related with ATP ties to the developing thorned end and afterward the ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP in the fibers. The ADP bound actin at that point disassociates from the sharp end and the actin disassociation from the short end of the microfilament. The two finishes are known as pointed end and thronged.
Polymerization of actin monomers starts with a particular advance called nucleation. Actin fiber prolongs or develops by the fuse of monomers at the two closures in a reversible manner. Each finish of the fiber develops at various rates and the spiked end can grow five to multiple times quicker when contrasted with the sharp end. Treadmilling is controlled in vitro by a few actin-restricting proteins40, including profilin, cofilin and CAP40. The dynamic idea of Actin fibers in the phone is constrained by an unmistakable gathering of proteins, called actin restricting proteins.
These proteins balance out the actin cytoskeleton inside the cell by restricting the fibers along their length or by cross-connecting them. Formins dimerize to frame a band molded structure that may work as a 'broken' cap, balancing out the early actin fiber and permitting controlled single-fiber growth70. We are eager to assist you out with the financing for this examination. Back to the pages you went to the paper you came From. ã1, £2, £3, £4.
Actins represent practically 20% of the whole cell protein. Among all the three sorts of proteins establishing the cytoskeleton, actin is amazingly rationed. Actins can be separated into two significant classifications - muscle-explicit actins and non-muscle actins. Tower, a new expansion to the nucleator class69, is thought to enroll four actin monomers, creating a novel single-abandoned actin tetramer that goes about as a seed for unbranched actin polymerization, while covering the 'pointed' end. The actin structure of actins is exceptionally preserved both at nucleotide and protein grouping level, for instance, actins of chicken and yeast show over 90% comparability in their amino corrosive arrangement.
Protein ADF/cofilin causes depolymerization of actin fibers by authoritative to ADP-actin at pointed end. Actin-restricting proteins, for example, profilin encourage the trading of ATP bound to actin with ATP. RBCs have been end up being valuable model frameworks for bits of knowledge into the cortical cytoskeleton because of their absence of film bound cores and organelles, microtubules and middle fibers. The actin-sceptrin network that comprises the cortical Cytoskeleton of R BCs is recognized by the presence of act in a generous sum.
The Cytoskeleton of Cells, by Dr. Andrew Stott and Dr. Richard Stott. 'The Cytoplasm of Cells: Aims to give bits of knowledge into cell association and capacity by seeing how actin, or actin packs, are coordinated in cells and how they are utilized for cell development and capacity, for example, adjustments fit as a fiddle and cell development.
Myosin is really an engine protein, that directs the transformation of compound energy into put away as ATP into mechanical energy. Actin is related with another significant protein-myosin and together they are answerable for producing different sorts of cell developments. Each muscle fiber is comprised of numerous myofibrils which are made out of dainty actin fibers and thick myosin fibers.
Each myofibril is spoken to as arrangement of a few individual rehashing contractile units known as sarcomeres which are essential for the cardiovascular and skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles found in vertebrates fall into three unmistakable classes skeletal muscles; which perform intentional developments, cardiovascular muscles; answerable for siphoning blood from the heart and the smooth muscles.
Middle of the road fibers are comprised of various sorts of proteins that express in various cell types. In excess of 65 distinct proteins comprising intermediate filaments are known and put in six gatherings, contingent upon amino corrosive succession homology. Test proof in people has demonstrated that nonattendance or articulation of freak keratin brings about extreme skin anomalies. It was seen that slight scouring of skin caused lysis of epidermal cells, prompting skin rankles, which indicated that presence of ordinary keratin is fundamental for mechanical solidarity to epithelial cells.
Gathering and Capacity of Middle fibers.
Conversely with actin fibers and microtubules, moderate fibers are comprised of various sorts of proteins that express in various cell types. Till now, in excess of 65 distinct proteins establishing halfway fibers are known and set in six gatherings, contingent upon amino corrosive grouping homology, in view of the phone types in which Ifs are found and based on sorts of proteins which make them, IFs contrast from tissue to tissue.
• Classes I and II incorporate keratins which are available in epithelial cells that cover the outside of the body. Class I keratins are known as 'acidic keratins' which class II keratins are known as unbiased or 'fundamental keratins' relying upon their substance nature. Trial proof in people has demonstrated that nonappearance or articulation of freak keratin brings about serious skin variations from the norm. It was seen that slight scouring of skin caused lysis of epidermal cells, prompting skin rankles, which indicated that presence of ordinary keratin is fundamental for mechanical solidarity to epithelial cells. This sickness is known as epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS), in which freak keratin restrains gathering of keratin fibers.
• Class III moderate fibers contains various proteins for example desman, vimentin and GFA (glial fibrillary acidic proteins). Desman protein is normal for muscle cells and GFA is available in glial cells around nerve cells. Vimentin is found in cells of connective tissue and furthermore in non-epithelial cells.
• Class IV IFs are known as neurofilament proteins and are available in nerve cells.
• Class V IFs have a place with atomic lamina A,B and C which are available in the internal surface of atomic layer.
Halfway fibers are available all through the cell as a complex organization spreading from plasma film on the external side to the core. They are connected with a few unmistakable parts of the cytoskeleton including actin fibers and microtubules. Neurofilaments are vital. moderate fibers of nerve cells and stay joined to both actin. fiber and miniature tubules and offer mechanical help and strength to other. cytoskeletal components of huge nerve cells. Desmosomes are areas of cell-cell contact at which the organization of middle. fibers is moored to the plasma film. The get together and dismantling of moderate fiber is directed by their phosphorylation for example by atomic lamins, which prompts complication of atomic lamina and deterioration of atomic encompass in mitosis. We realize that cell-cell bond assumes significant part in tissue morphogenesis, development and movement and so on of cells.
Microtubules
Microtubules are the biggest in size among all cytoskeletal segments. In eukaryotic cells, microtubules are for the most part gathered into two classifications: axonemal microtubules and cytoplasmic microtubules-the two of which contrast enormously in their structure and association.
Axonemal microtubules
They are incredibly steady and exceptionally coordinated microtubules inside different structures for example cilia, flagella, basal bodies and help in cell development. The axoneme or focal shaft of cilia and flagella is comprised of axonemal microtubules masterminded in exceptionally requested example in relationship with explicit proteins.
Cytoplasmic microtubules
They speak to some degree approximately organized yet powerful organization of microtubules. They help in doing an assortment of cell capacities for example the support of axons in creature cells, in deciding course of the statement of cellulose microfibrils during cell lengthening. Likewise, cytoplasmic microtubules assume a basic part in the arrangement of mitotic and meiotic axles during cell division. Moreover, these microtubules oversee the development of different organelles and vesicles by shaping a coordinated organization of strands.
Structure of microtubules
Microtubules are infact long, straight empty chambers with an inward measurement of 15 nm and an external width of 25 nm. They broaden upto shifted length inside the cell, going from numerous micrometers for example axonemal microtubules, to as short as 20 nm. The mass of empty chamber of a microtubule comprises of longitudinal varieties of protofilaments masterminded in straight design. By and large, 13 protofilaments are available related horizontally with one another to shape a roundabout chamber, encasing the empty community or lumen.
The building squares of a protofilament are heterodimers of a globular protein known as tubulin. Each heterodimer or a subunit of a protofilament is comprised of one atom of α-tubulin and a solitary particle of β-tubulin. Both α and β tubulin particles tie to one another in a non-covalent way when they are combined and are hard to separate from that point. In a protofilament, tubulin heterodimers stay orchestrated in a head to design to shape a direct fiber.
Primary investigation has uncovered that in spite of the fact that α and β tubulin atoms show just 40% arrangement closeness at amino corrosive level, the three dimensional structures of both is practically indistinguishable. All the tubulin dimers in a microtubule are arranged the very way in such a way that the α tubulins face towards a similar end. This direction of tubulin dimers guarantees that the two finishes of a protofilament remain fundamentally and artificially unique in relation to one another, which offers ascend to extremity in a protofilament and therefore in a microtubule itself.
Get together and part of microtubules
Microtubules are shaped by the reversible expansion of tubulin dimers to frame protofilaments which partner together to offer ascent to microtubules. Similarly as if there should be an occurrence of actin fibers, the accessible convergence of tubulin dimers choose the development of microtubules, which polymerize in presence of high tubulin fixation and depolymerize at low tubulin focus. In the middle of the high and low focus exists a specific grouping of tubulin dimers at which the pace of microtubule get together is actually adjusted by its dismantling. This specific grouping of tubulin dimers is known as 'basic fixation'
The main capacity performed by microtubules in eukaryotic cells is the vehicle of macromolecules, film bound vesicles and organelles. Cytoplasmic organelle transport has been concentrated in squid nerve cell axons, which are enormous in size. Medications, for example, vinblastine, which totals tubulin dimers make endoplasmic reticulum contract towards the center of the cell, which implies that its communication with miniature tubules is significant for keeping up its unique shape. Kinesin I is answerable for shipping mRNA of actin inside fibroblasts, while dynein moves specific RNAs starting with one area then onto the next in Drosophila undeveloped organism.
The steadiness of Golgi mechanical assembly is dared to be because of the activity of kinesin. I, which extends it towards the limit of the cell. Contrastingly, cytoplasmic dyne in is viewed as engaged with keeping up the situation of Golgi mechanical assembly in the focal point of the cells.






0 Comments
We are pleased to see you here! Please mention your suggestion or query in the comments box below.