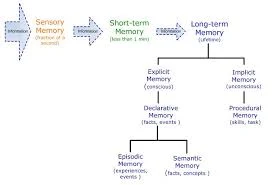
Memory is the measure of recently learned material that has been held. Subsequently, maintenance is another name for memory. There are two essential types of maintenance: procedural and explanatory.
1. Procedural memory is the way to play out an activity, in succession. Athletic abilities are one illustration of procedural memory. We get familiar with the essentials, practice them again and again, and afterward they appear to stream normally when we are in a game. Practicing for a moving or melodic presentation would be different instances of procedural memory. Ordinary models may be recollecting how to tie our shoes, drive a vehicle, or jump on the web.
2. Declarative memory includes memory for realities, ideas and occasions as opposed to strong techniques. Revelatory memory might be rambling or semantic.
3. Semantic maintenance is for the kind of information we partner with books and school: names, dates, and numbers. Be that as it may, it can likewise incorporate individual data, for example, phone numbers and addresses.
4. Episodic maintenance includes recollections for explicit occasions. Flashbulb recollections are of especially distinctive occasions that continue in our psyches. A portion of these occasions became flashbulb recollections since they were so significant, or associated with extraordinary feelings (delight, torment or pride).
Which means and Nature:
The memory is characterized as 'the ability to store encounters and to carry them into the field of cognizance at some point after the experience has happened'. Our psyche has the intensity of saving encounters and intellectually getting them at whatever point such a movement helps the forward advancement of the existence cycle.
Presentation
Memory is one of the significant intellectual cycles. Memory includes recollecting and failing to remember.
These resemble two countenances of a coin. Despite the fact that these two are against one another essentially, they assume a significant function in the life of a person.
Recalling the charming encounters fulfills living, and then again recollecting terrible encounters makes living despondent and hopeless. So here failing to remember causes individual to fail to remember undesirable and horrendous encounters and recollections and keeps him cheerful.
Along these lines, recollecting the charming and failing to remember the-terrible both are fundamental for typical living. On account of students, recollecting is significant, in light of the fact that without memory there would be no learning.
In the event that learning needs to advance, recollecting of what is now discovered is key, in any case each time the student needs to begin from the earliest starting point.
The saved experience has a solidarity, an association of its own and it colors our current experience.
Cycle
Memory is one of the focal segments of human discernment, remembering the capacity to take for data, measure it, store it, and in this manner recover it when fundamental. In this manner the center cycles of memory are encoding, stockpiling, and recovery:
1. Encoding: Processing data, coordinating it, and checking it for capacity
2. Storage: Holding data after some time in what is in a perfect world a coordinated stockpiling framework
3. Retrieval: Calling put away data to awareness
In any case, as expressed above we have an idea that memory is a solitary cycle, yet an examination of it uncovers contribution of three unique exercises learning, maintenance and recollecting.
Learning:
This is the principal phase of memory. Learning might be by any of the techniques like impersonation, verbal, engine, reasonable, experimentation, understanding, and so forth Subsequently, whatever might be the kind of learning; we should give our consideration to hold what is found out. A decent learning is essential for better maintenance.
Maintenance:
Maintenance is the way toward holding as a top priority what is found out or experienced previously. The educated material must be held to gain ground in our learning. Analysts are of the feeling that the scholarly material will be held in the mind as neural follows called 'memory follows', or 'engrams', or 'neurograms'.
At the point when great learning happens – clear engrams are shaped, so they stay for long time and can be recollected by initiation of these follows at whatever point fundamental.
Recollecting:
It is the way toward bringing back the put away or held data to the cognizant level. This might be perceived by exercises, for example, reviewing, perceiving, relearning and reproduction.
Reviewing:
Reviewing is the way toward imitating the previous encounters that are absent. For instance, reviewing answers in the assessment corridor.
Perceiving:
It is to perceive an individual seen before, or the first things seen before, from among the things of a similar class or classification which they are stirred up.
Relearning:
Relearning is otherwise called sparing strategy. Since we measure maintenance regarding sparing in the quantity of redundancy or the time needed to relearn the task. The distinction between the measure of time or preliminaries needed for unique learning and the one needed for relearning demonstrates the measure of maintenance.
Remaking:
Remaking is generally called revision. Here the material to learn will be introduced in a specific request and afterward the things will be confused up or rearranged altogether and introduced to the person to revamp them in the first request where it was introduced.
Kinds of Memory:
There are five sorts of memory. These are characterized based on paces of rot of the data.
a. Sensory memory:
In this sort of memory, the data got by the receptors will stay there for an extremely brief period like couple of moments. For instance, the picture on the screen of a TV may give off an impression of being in our eyes for a small amount of time in any event, when it is turned off, or the voice of an individual will be shivering in our ears even after the voice is stopped.
b. Short-term memory (STM):
As per numerous investigations, in STM the memory stays in our cognizant and pre-cognizant level for under 30 seconds. Later on this will be moved to long haul memory.
c. Long-term memory (LTM):
LTM has the limitless ability to store data which may stay for quite a long time, months, a long time or lifetime.
d. Eidetic memory:
It is generally considered photographic memory in which the individual can recall a scene or an occasion in a photographic detail.
e. Episodic memory:
This is generally called semantic memory which is associated with scenes of occasions. The occasions are put away as scenes and reviewed completely in the way of a succession.
SORTS OF REMEMBERING
There are three primary sorts of memory. The sorts are: 1. Roundabout Memory 2. Semantic Memory
3. Procedural Memory.
Type 1. Rambling Memory:
William James' ideas of essential and optional memory were changed by Endel Tulving to rambling memory and semantic memory. Roundabout memory is supposed to be the store of the personal occasions in the life of the individual and is coordinated by the time, space and different characteristics of the particular occasion or occasions.
What is befalling you now, that of which you are cognizant is the impression of what is being put away in essential and furthermore the current substance of the verbose memory. For instance, in the event that you return and describe about a mishap you have seen, it is wordy memory. What one can construe from this portrayal is the basic cycle – the rambling memory.
Type 2. Semantic Memory:
Semantic memory then again, stores an assortment of connections between occasions which could possibly have gone through rambling memory yet stores the assortment of connections between occasions. At the end of the day, semantic memory incorporates the coordinated information we have about language, for example words and other verbal images, their memory and the relations between them, rules, formulae and the control of these images, ideas and relations.
For instance, One needs to utilize explicit words to portray which vehicles impacted, (regardless of whether it is a Lorry, Fiat, Ambassador or some different vehicles), with what speed they were voyaging, (generally as far as kilometers every hour), who defied the guidelines, whether the lorry-driver needed to overwhelm the vehicle or the other way around, etc.
Wordy memory is self-portraying and more close to home and, thusly varies starting with one individual then onto the next in light of the fact that their encounters are unique. In any case, the semantic memory framework is with the end goal that it needs to utilize language or control words based on acknowledged guidelines.
Semantic memory is pretty much open and the memory of one individual contains generally a similar kind of data as the other, however the example of association may contrast. For example, if two people have visited Kanyakumari, their wordy recollections may contrast on account of their experience. In any case, both will understand what the forte of the spot is for example how far an away the stone cut sanctuary is constructed, why it was fabricated, what is the importance of sand, ocean, dusk, dawn, and so forth
As indicated by Tulving's model, contribution to semantic memory is through verbose memory and each occurrence of the utilization of semantic memory establishes a section into long winded memory.
Type 3. Procedural Memory:
At times, the term procedural memory is likewise utilized notwithstanding the conditions of verbose memory and semantic memory. This is otherwise called aptitude memory. Expertise memory for the most part includes how to get things done in a mind boggling activity.
For instance, when one is driving a vehicle or a bike, this includes numerous exercises to be done in an arrangement. Truth be told, there are numerous exercises which include a recovery of scholarly and stockpiled data and this occurs in a programmed and oblivious way.
Aside from three sorts of memory, wordy, semantic, and procedural, there are numerous exercises associated with all these. For instance, in the event that we are playing a chess game, this includes semantic memory, as what the circumstance currently is regarding scores – semantic memory, maybe, recalling the sorts of dispositions one may have had in th








0 Comments
We are pleased to see you here! Please mention your suggestion or query in the comments box below.